All About Hair

Posted By Edge
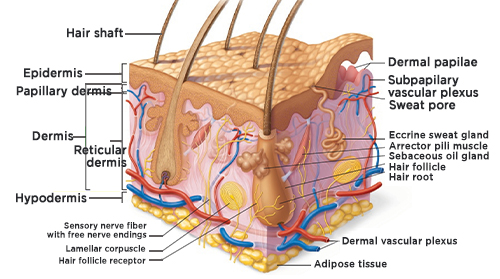
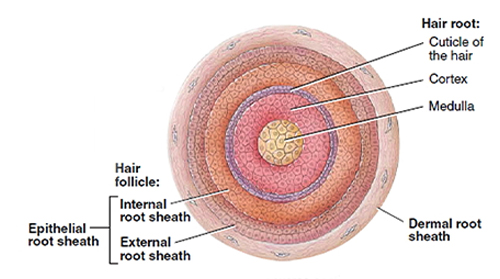
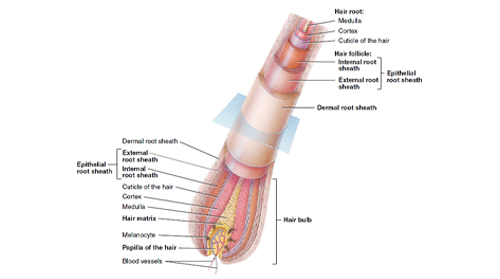
| Hair is one of the most interesting, mysterious, and complex things we have. It's not just a thing on our head that can make us feel confident and beautiful, keeps us warm, and protects us from the elements; it's also an indicator of our health, personality, and even how we feel about ourselves. Not to mention it's probably the first thing people notice when they meet us! But what is hair? How does it work? How does it affect us? We'll be exploring all these questions in this series of posts, starting with a breakdown of what hair actually is: Hair Its a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. It is a major component of our body’s outer layer, which is made up of three layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Hair provides thermal insulation for the body, and prevents hydration loss and evaporation; it also serves as a sensory organ and as a secondary sexual characteristic in mammals. The primary function of hair is to provide an evolutionary advantage by increasing the surface area of the skin exposed to sunlight and thus allowing more efficient thermoregulation. Hair also increases drag, which aids in swimming. The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures:
Hair’s Natural Color All natural hair colors are the result of two types of hair pigments. Both of these pigments are melanin types, produced inside the hair follicle and packed into granules found in the fibers. Eumelanin is the dominant pigment in brown hair and black hair, while pheomelanin is dominant in red hair. Blond hair is the result of having little pigmentation in the hair strand. Gray hair occurs when melanin production decreases or stops. Hair’s Classifications There are various systems that people use to classify their curl patterns. Being knowledgeable of an individual's hair type is a good start to knowing how to take care of one's hair. Andre Walker System The Andre Walker Hair Typing System is the most widely used system to classify hair. The system was created by the hairstylist of Oprah Winfrey, Andre Walker. According to this system, there are four types of hair: straight, wavy, curly, and kinky.  Andre Walker Hair Types
It is possible, and quite normal to have more than one kind of hair type, for instance having a mixture of both type 3a & 3b curls. The Importance of Hair Your hair is important to your overall health and well-being because it is one of the first aspects that others may notice about you. How healthy and vibrant your hair is can tell someone what type of person you are, and how you feel about yourself. Healthy hair is a sign of confidence and allows others to view you in a positive light. But that's not all. It also has an important function on our body.
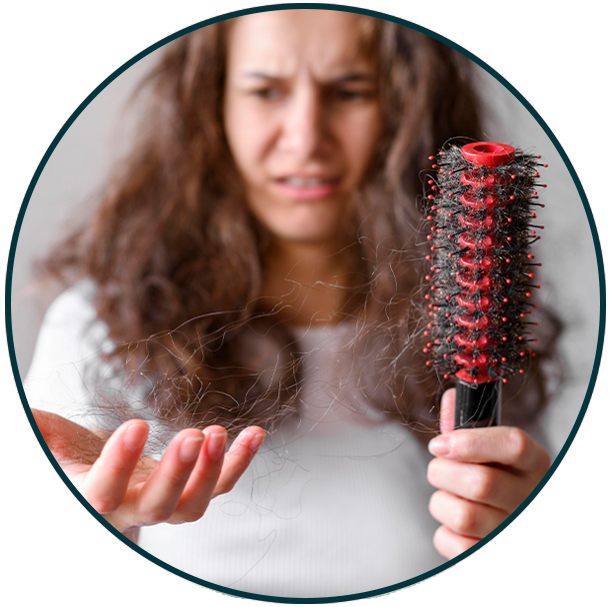
What damages our hair? If you're like most people, you probably take your hair for granted. You wash it, brush it, and then forget about it until the next time you need to style or shampoo it. But if you want to keep your hair looking healthy and beautiful, it's important to know some of the things/factors that can damage your locks. Here are some of the main culprits:
Ingredients to watch out in your hair care products. It's no secret that most of us don't like the idea of having harmful chemicals on our skin. But what about when we put them in our hair? Unfortunately, many shampoos, conditioners, and other products contain chemicals that can be harmful to your health and the environment. Here's a look at some common chemicals found in hair care products and how they affect your body: Parabens Parabens are used as preservatives in many cosmetic and personal care products, including make-up, moisturizers, hair care products and shaving products. The problem is, having parabens in products that are designed to be absorbed through your skin isn’t exactly a good thing. It can trigger irritation and allergic reactions in the skin, especially to sensitive, damaged, or broken skin. It can be especially inflammatory to those with pre-existing conditions of psoriasis, eczema, or a pattern of contact dermatitis. It can also cause a number of problems for your hair including drying, irritating your scalp, fading your color, and even hair loss. They are generally used at concentrations of 0.5% or less but since they are generally unsafe, it is best to avoid parabens until proven otherwise Studies about this Ingredient:Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) Sulfates can leave the hair dry and unhealthy, causing your hair to lose the moisture it needs. It can also dry the scalp and cause irritation. The safety assessment study of SLS found that it was not harmful when used briefly and then rinsed from the skin, as with shampoos or soaps, and should not exceed 1 percent concentration of SLS. Though it is an irritant, it's not a carcinogen. The risks are minimal when these products are used correctly—that is, in short applications that get rinsed off right away. Estimates for non-prescription drugs range from 0.106 to 0.21 mg/kg bw for adults and from 0.035 to 0.14 mg/kg bw for children. The ranges provided correspond to taking one capsule/tablet a day to the maximum recommended daily dose. Studies about this Ingredient:https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/what-is-sodium-lauryl-sulfate#possible-dangers Phthalate Phthalates are found in a wide range of cosmetics and personal care products, including nail polishes, hair sprays, aftershave lotions, cleansers and shampoos. However, some phthalates have been linked to adverse health effects, such as hormone disruption, reproductive toxicity, and developmental toxicity. The most commonly used phthalates in cosmetics are:
Must not contain more than 1 000 mg/kg of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP) or benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) when tested in accordance with a method that conforms to good laboratory practices. Studies about this Ingredient:https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-188/page-1.html#h-832558 Alcohol Some consumers buy "alcohol-free" hair care or skin products, believing that alcohol dries out their scalps or faces. In cosmetic labeling, the term alcohol used by itself refers to ethyl alcohol. But those Alcohol-free products may still contain other alcohol such as cetyl, stearyl, cetearyl, or lanolin alcohol. These are known as fatty alcohols, and their effects on the skin are quite different from those of ethyl alcohol. Isopropyl alcohol, which some consumers may think of as drying the skin, is rarely used in cosmetics. Fatty alcohol is categorized as a "good" alcohol and is obtained plant fatty acids. They are non-toxic, well tolerated by the skin and biodegradable. Studies about this Ingredient:https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics/cosmetics-labeling-claims/alcohol-free Triclosan (also known as Antimicrobials) Triclosan is used in cosmetics as a preservative to prevent or slow down microbial growth and protect products from spoilage. This ingredient is also used in over-the-counter drugs and other consumer products. Health Canada considers triclosan to be safe when used in cosmetics at a concentration of up to 0.03% in mouthwashes and 0.3% in other cosmetic products like soaps. Studies about this Ingredient:https://www.chemicalsubstanceschimiques.gc.ca/fact-fait/triclosan-eng.php How Heat and Pollution Could Be Stressing Your Hair. Large suspended particles, small airborne particles, smoke, and gaseous pollution reach the scalp and hair, causing irritation and damage. With pollution increasing in modern life, cases are becoming more pronounced and serious. These pollutants can lead to excess sebum in the scalp which produces hair follicles to become clogged and may even stunt hair growth. Air pollutants bring out frizz and dryness while being exposed to UV rays can cause discoloration, and brittleness, and can damage the cuticle producing split ends. Hair loss caused by contamination is related to nano-particles suspended in the air, as well as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (highly present in the smoke from car exhaust, asphalt, industrial smoke, etc.). Both will damage the hair by inducing oxidative stress in the follicular units. How Water Pollution Could Affect Your Hair (or Skin). If you’ve taken a shower at a place other than your house, maybe a hotel, or a friend’s house, you may notice that your hair feels different. Common water contaminants can affect your hair’s look, feel, and general health. Hard water means water containing high levels of minerals like calcium and magnesium. In some places, the water that comes directly to the homes of people, contains a number of minerals and oxidizers. A little bit of it is okay and natural, but when the percentage of these minerals and oxidizers rise, they begin to harm the hair and the scalp. Hard water affects the hair in many ways, including:
Safe limit to use Pollutant Water
When addressing a hard water problem, the first thing to do is get an in-home water test (use ph test strips). The test helps to check the actual level of hardness-causing minerals in your water.
You mustn’t take the effects of hard water on your hair and skin lightly. Having proper knowledge of the issue can help you take the right steps towards softening the water in your home. Reference:https://www.uswaterfilter.org/does-water-quality-have-any-effect-on-hair/ Why do we need to take care of our hair? The answer is simple: because it's an important part of what makes us human. There are a lot of reasons why you should take care of your hair. You might think that it's just a matter of looking good and feeling confident, but the reality is that your hair is an extension of your health. You don't have to be a scientist to know that the quality of your hair reflects the quality of your health. And when you think about it, that makes sense—since hair is made up mostly of protein, it's basically a reflection of your diet and how well you're taking care of yourself. So remember: taking care of our hair isn't just about vanity—it's about maintaining our overall wellness! At Eternal Skin Care, we believe that everyone has a place in our community. We are committed to Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion. We believe that everyone deserves to feel safe and welcome in their community, and we're happy to share these products with the world knowing that they can be enjoyed by all kinds of people. We have a wide range and variety of products available, all designed for different needs and also to make you feel great. |
For those who have...
For those who have...
For those who are struggling with...
For those who are struggling with...
If you want your hair to have...
If you want your hair to have...